18
2025
-
09
SFP vs QSFP vs GBIC: Key Differences You Should Know
Author:
Introduction
In modern networking, transceiver modules play a vital role in enabling high-speed communication across enterprises, data centers, and telecom networks. Among the most commonly discussed options are SFP (Small Form-factor Pluggable), QSFP (Quad Small Form-factor Pluggable), and GBIC (Gigabit Interface Converter).
While all three serve the same general purpose—transmitting and receiving data over fiber or copper—they differ significantly in size, speed, and use cases. This article provides a detailed comparison of SFP vs QSFP vs GBIC to help network engineers, IT managers, and procurement professionals make informed decisions.
What is SFP?
Definition: A compact, hot-swappable transceiver used in switches, routers, and servers.
Speed: Typically supports 1G (SFP), 10G (SFP+), and up to 25G.
Use Cases: Enterprise networks, data centers, and campus networks.
Key Advantage: High port density due to its small form factor.

What is QSFP?
Definition: A “quad” version of SFP, designed to support higher data rates.
Speed: 40G (QSFP+), 100G (QSFP28), and 400G (QSFP-DD).
Use Cases: Data centers requiring massive bandwidth, cloud service providers, and backbone networks.
Key Advantage: Higher throughput per port, reducing equipment footprint.
What is GBIC?
Definition: Gigabit Interface Converter, an older standard for transceivers.
Speed: Typically supports up to 1 Gbps.
Use Cases: Legacy systems in older enterprise networks.
Key Advantage: Hot-swappable, but much larger compared to SFP.

Technical Comparison: SFP vs QSFP vs GBIC
| Feature | SFP | QSFP | GBIC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Size | Very compact (small form) | Slightly larger than SFP | Large (obsolete by today’s standards) |
| Speed | 1G, 10G, 25G | 40G, 100G, 400G | Up to 1G |
| Port Density | High (fits more ports per switch) | Moderate (higher speed, fewer ports needed) | Low (large size limits density) |
| Compatibility | Widely supported across vendors | Common in modern high-speed devices | Mostly obsolete |
| Cost | Affordable (esp. third-party) | Higher cost due to advanced speeds | Rare, costly if still sourced |
| Use Case | General networking | Data center backbone, HPC clusters | Legacy enterprise equipment |
SFP vs QSFP: Which One Should You Choose?
Choose SFP/SFP+ if:
You need 1G or 10G connectivity.
Your network requires high port density.
You are upgrading enterprise or campus networks.
Choose QSFP if:
You need 40G/100G/400G connectivity.
You’re managing a data center with massive east-west traffic.
You want to future-proof for cloud and 5G networks.

SFP vs GBIC: Why SFP Replaced GBIC
Smaller size – SFP offers more ports per switch compared to bulky GBICs.
Higher scalability – SFP supports 1G to 25G, while GBIC is limited to 1G.
Market adoption – Most networking vendors have phased out GBIC.
👉 In short: GBIC is legacy, SFP is mainstream, QSFP is high-performance.
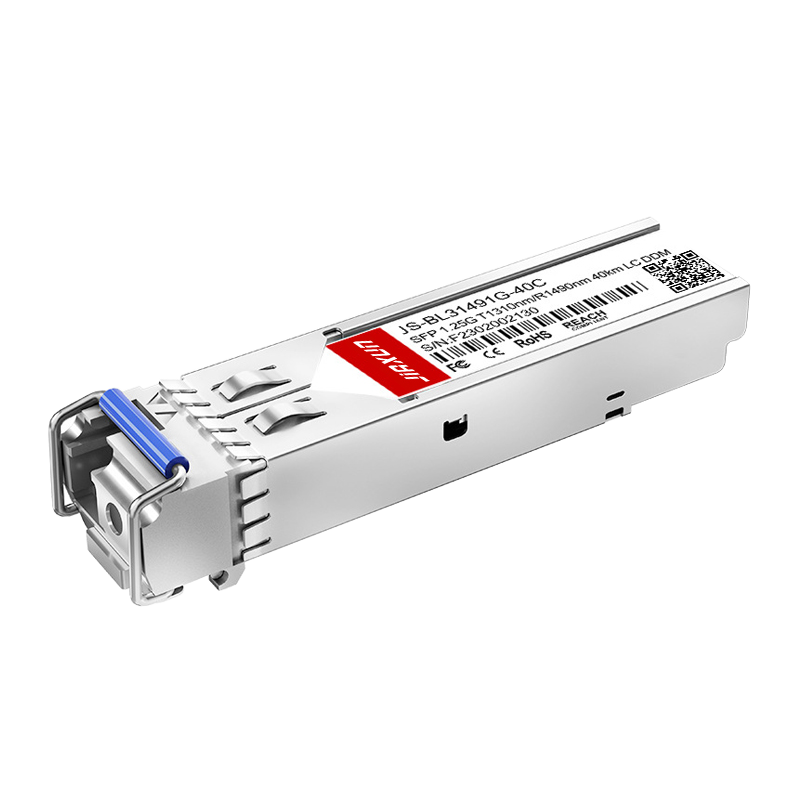
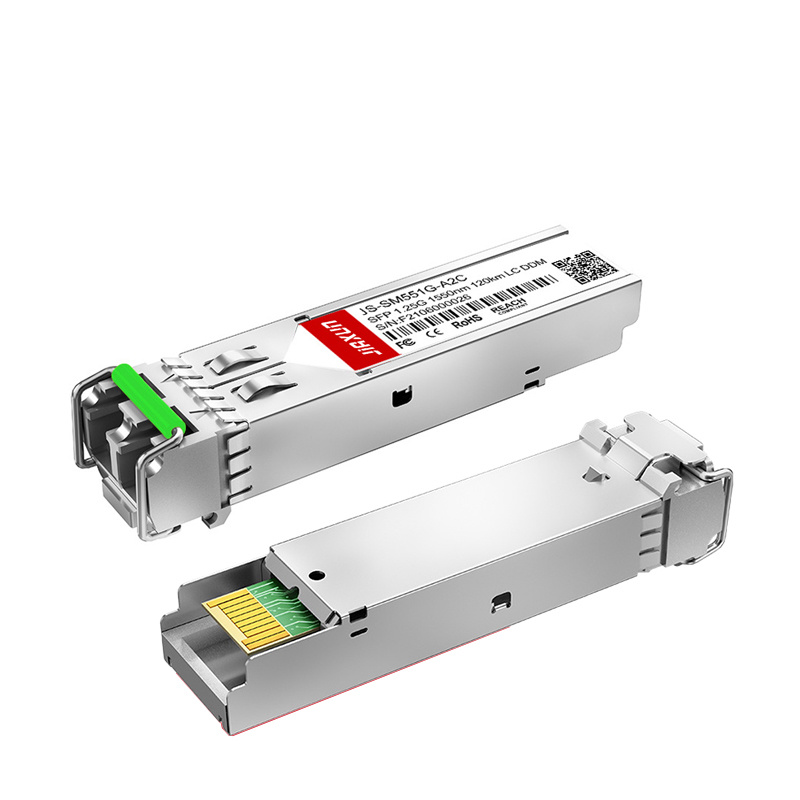
Product Highlight: Reliable 10G SFP+ Solution
For organizations seeking a cost-effective yet high-performance SFP+ module, the JS-SM5510-A2C Duplex LC SMF Optical Transceiver (1550nm, 10G SFP+) is a solid option.
Long-distance transmission over single-mode fiber.
Duplex LC connector for easy integration.
Designed for enterprise and telecom-grade applications.
This makes it an excellent choice for networks that require reliable 10G performance without the high cost of OEM-branded modules.
Conclusion
Choosing between SFP, QSFP, and GBIC depends largely on your network’s speed requirements, scalability needs, and budget.
SFP remains the standard for 1G/10G enterprise networking.
QSFP dominates in high-speed environments like data centers.
GBIC is largely obsolete and should only be considered for legacy systems.
By understanding these differences, you can make smarter purchasing decisions and ensure your network is both cost-effective and future-ready.
SFP,QSFP,GBIC
Previous Page
18
2025-09
SFP vs QSFP vs GBIC: Key Differences You Should Know
16
2025-09
Optics Transceiver Module: Key Types, Applications, and Buying Guide
15
2025-09
How to Choose the Right RJ45 Connector for Your Network: A Complete Guide
13
2025-09
What is an RJ45 connector? A comprehensive analysis and installation guide
09
2025-09
How to Choose the Right Industrial-Grade RJ45 Connector? Selection Guide and Precautions
09
2025-09
RJ45 Connector Buying Guide: Why High-Quality Connectors Are the Key to Network Stability?
08
2025-09
5 Ways Integrated Magnetic RJ45 Connectors Simplify PCB Layout and Save Space
Contact Us
Factory add: NO.54. Jinhu South Road, Chenjiang Town, Zhongkai Hi-tech Zone, Huicheng District, Huizhou city, China
Telephone:0752-2099791
Office add: B901-1, Silver Star Hi-Tech Building, No. 1301 Guanguang Road, Longhua District, Shenzhen, China
Website:www.jiaxunzg.cn
Telephone:0755-81752121
Fax: 0755-81752963
Mailbox:sales1@jiaxunzg.cn
Mailbox:sales2@jiaxunzg.cn
Mailbox:sales3@jiaxunzg.cn
Copyright © 2024 Jiaxun (Huizhou) Intelligent Technology Co., Ltd. Privacy Policy